The United States Congress is a vital institution in the American political system. As the legislative branch of the federal government, it plays a crucial role in shaping laws, policies, and the nation’s direction.
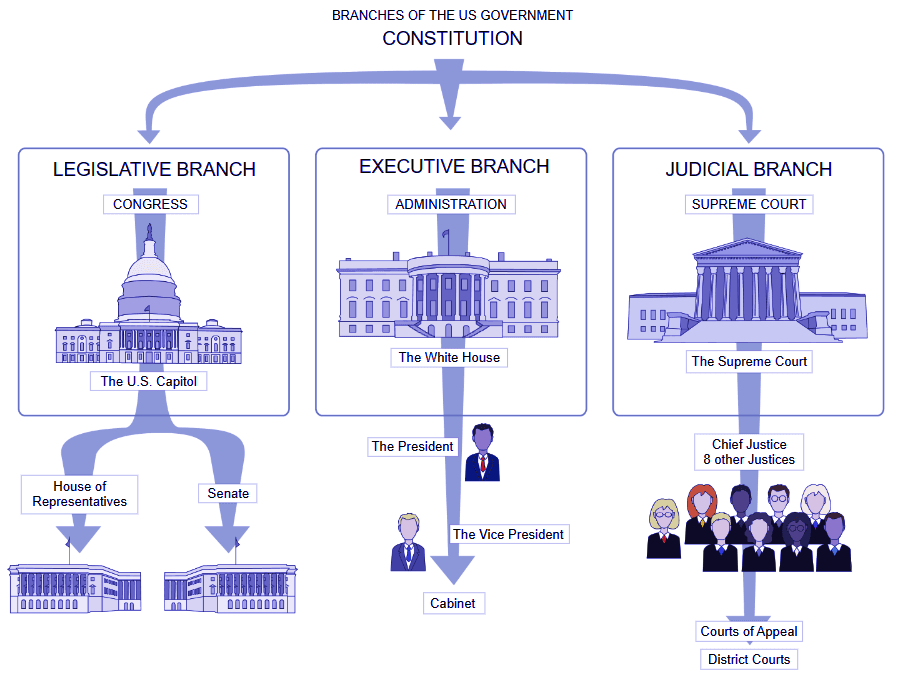
Let’s delve into the key aspects of Congress:
1. The Legislative Process: From Bills to Laws
- Bills are introduced in either the House of Representatives or the Senate.
- Committees review, amend, and refine bills before they reach the floor for debate.
- Both chambers must pass identical versions of a bill for it to become law.
- The president can sign or veto a bill, and Congress can override a veto with a two-thirds majority.
2. Congressional Committees: The Engines of Policy
- Standing committees focus on specific policy areas (e.g., finance, foreign affairs).
- Select committees investigate specific issues (e.g., ethics violations, intelligence).
- Committee members conduct hearings, gather evidence, and propose legislation.
3. Leadership and Decision-Making
- The Speaker of the House and the Senate Majority Leader wield significant influence.
- Leadership positions determine legislative priorities and guide party agendas.
- Committees, caucuses, and individual members also shape policy decisions.
4. Oversight and Accountability
- Congress monitors the executive branch, agencies, and programs.
- Oversight includes hearings, investigations, and reporting.
- Transparency and checks on government power are essential.
5. Budgeting and Appropriations
- Congress controls federal spending through the budget process.
- Appropriations bills allocate funds to various programs and agencies.
- Balancing priorities and fiscal responsibility is a constant challenge.
6. Congressional Caucuses: Advocacy and Influence
- Caucuses are informal groups of legislators with shared interests.
- They advocate for specific issues (e.g., climate change, veterans’ rights).
- Caucuses build coalitions and influence policy debates.
7. Historical Significance and Turning Points
- Reflect on pivotal moments in congressional history (e.g., Civil Rights Act, impeachment proceedings).
- Understand how historical context shapes legislative decisions.
8. Challenges and Debates
- Explore current debates, such as filibusters, partisanship, and campaign finance reform.
- Consider proposed reforms to enhance congressional effectiveness.
9. Congress and Representation
- Members represent diverse constituencies and balance local and national interests.
- Constituent services, town halls, and communication are essential.
10. The Future of Congressional Innovation
- Discuss emerging trends, technology adoption, and adapting to societal changes.
Remember, Congress is a dynamic institution that reflects the will of the people. By understanding its powers and processes, we can actively engage in our democracy.